Latest posts
-
New spinout: PvP Biologics!
We are happy to congratulate Ingrid Swanson Pultz, an IPD Translational Investigator, and Clancey Wolf, a Research Scientist, on PvP Biologics‘ spinout! The news was announced this morning and has been circulated through various outlets. The company, created in 2015, is focusing on advancing KumaMax, a gluten-fighting enzyme that could…
-
Arzeda scales its automated molecule development pipeline
Seattle-based Arzeda, a computational and synthetic biology company that was spun out from the University of Washington labs of Prof. David Baker, recently announced that its high-throughput, automated pipeline for protein engineering and pathway discovery had been validated by the production of two keystone molecules. The announcement is a major…
-
Unleashing the Power of Synthetic Proteins
Published today in Science Philanthropy Alliance, David Baker, Director of the Institute for Protein Design describes how the opportunities for computational protein design are endless — with new research frontiers and a huge variety of practical applications to be explored, from medicine to energy to technology. This is an exciting time as we…
-
Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Day and New Foldit puzzle
Today is Limb Girdle Muscular Dystrophy Day, and the Institute for Protein Design is collaborating with the Jain Foundation and Foldit community to to model the structure of human dysferlin protein (DYSF), an important protein for normal muscle function. Numerous mutations in the gene that encodes DYSF protein are known…
-
Hyper-stable Designed Peptides and the Coming of Age for De Novo Protein Design
Small constrained peptides combine the stability of small molecule drugs with the selectivity and potency of antibody-based therapeutics. However, peptide-based therapeutics have largely remained underexplored due to the limited diversity of naturally occurring peptide scaffolds, and a lack of methods to design them rationally. New computational design and wet lab methods…
-
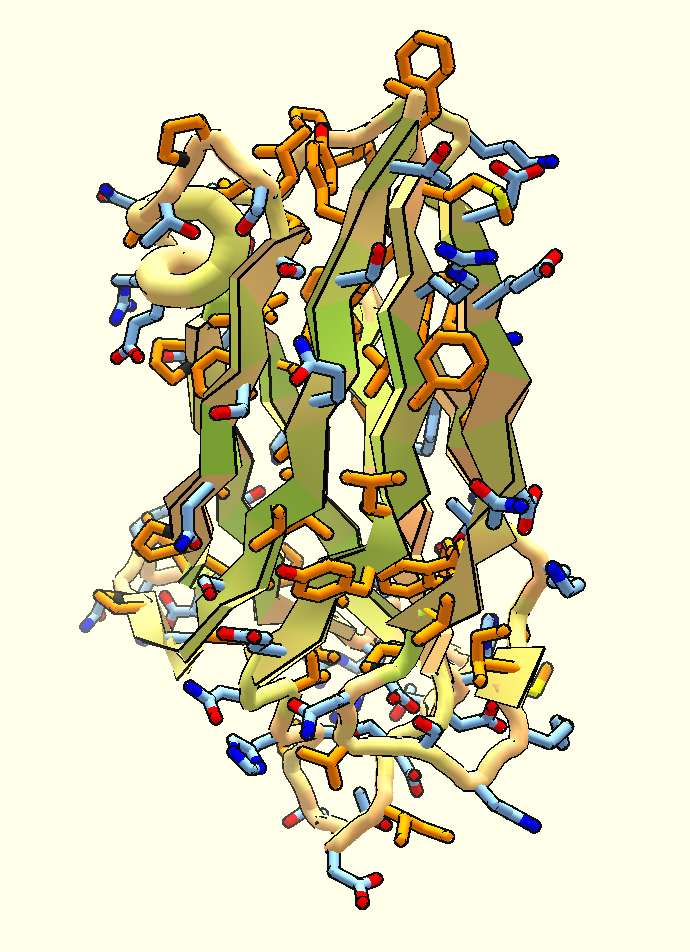
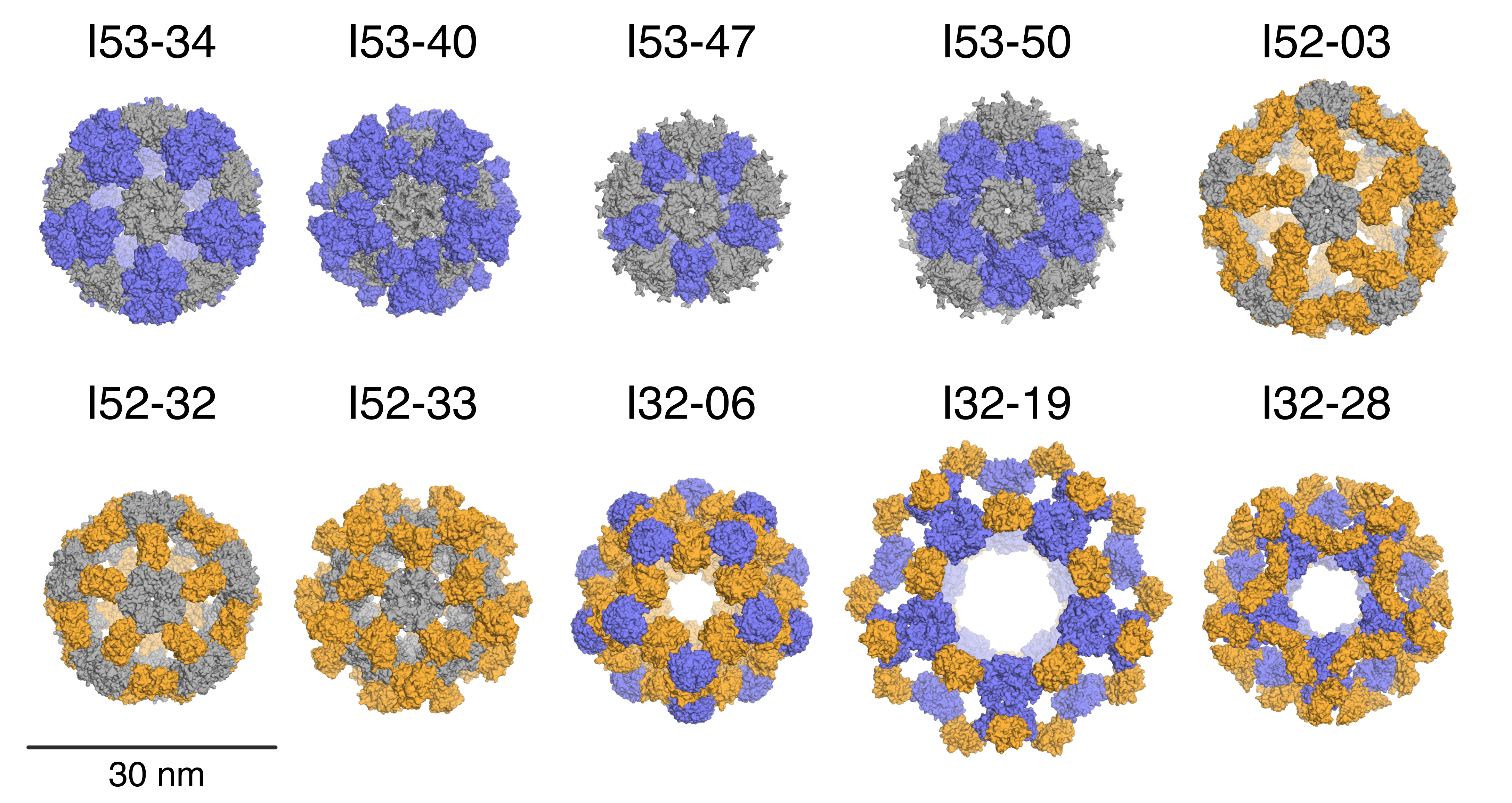
Designed Protein Containers Push Bioengineering Boundaries
Earlier this month, Baker lab researchers reported the computational design of a hyperstable 60-subunit protein icosahedron in Nature (Hsia et al); icosahedral protein structures are commonly observed in natural biological systems for packaging and transport (e.g. viral capsids). The described design was composed of 60 trimeric protein building blocks that…
-
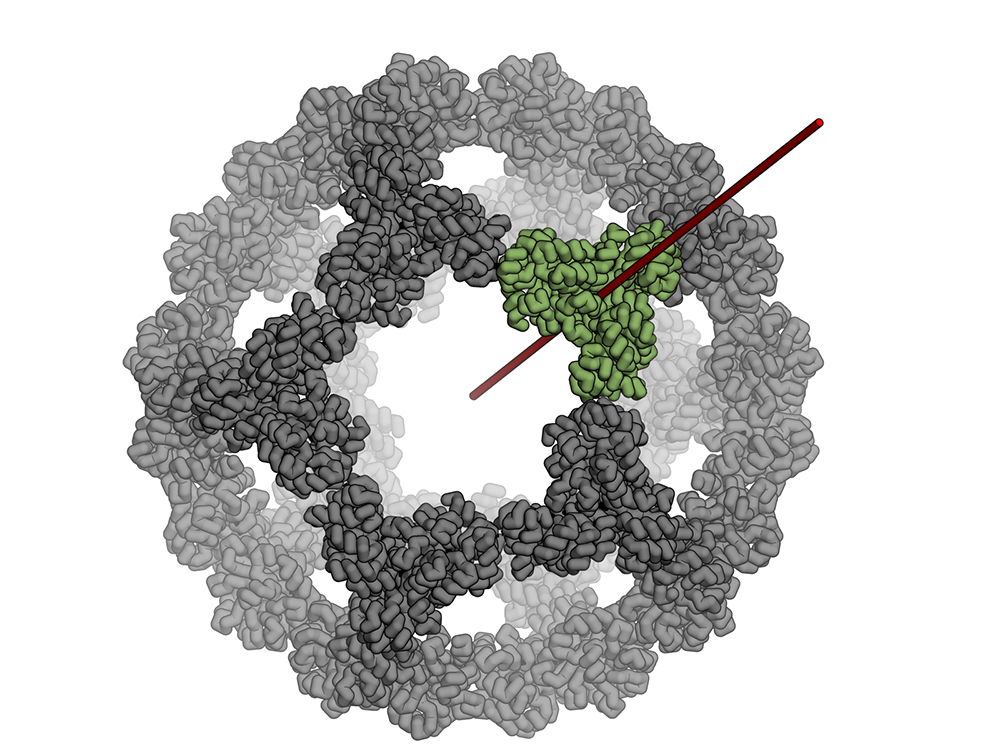
Icosahedral protein nanocage – new paper and podcast
The Baker lab, in collaboration with Neil King, Trisha Davis and Tamir Gonen’s labs, recently had a paper published in Nature about a stable icosahedral nanocage whose applications could span anywhere from drug delivery to vaccine design! The title is “Design of a hyperstable 60-subunit protein icosahedron” and it was…
-
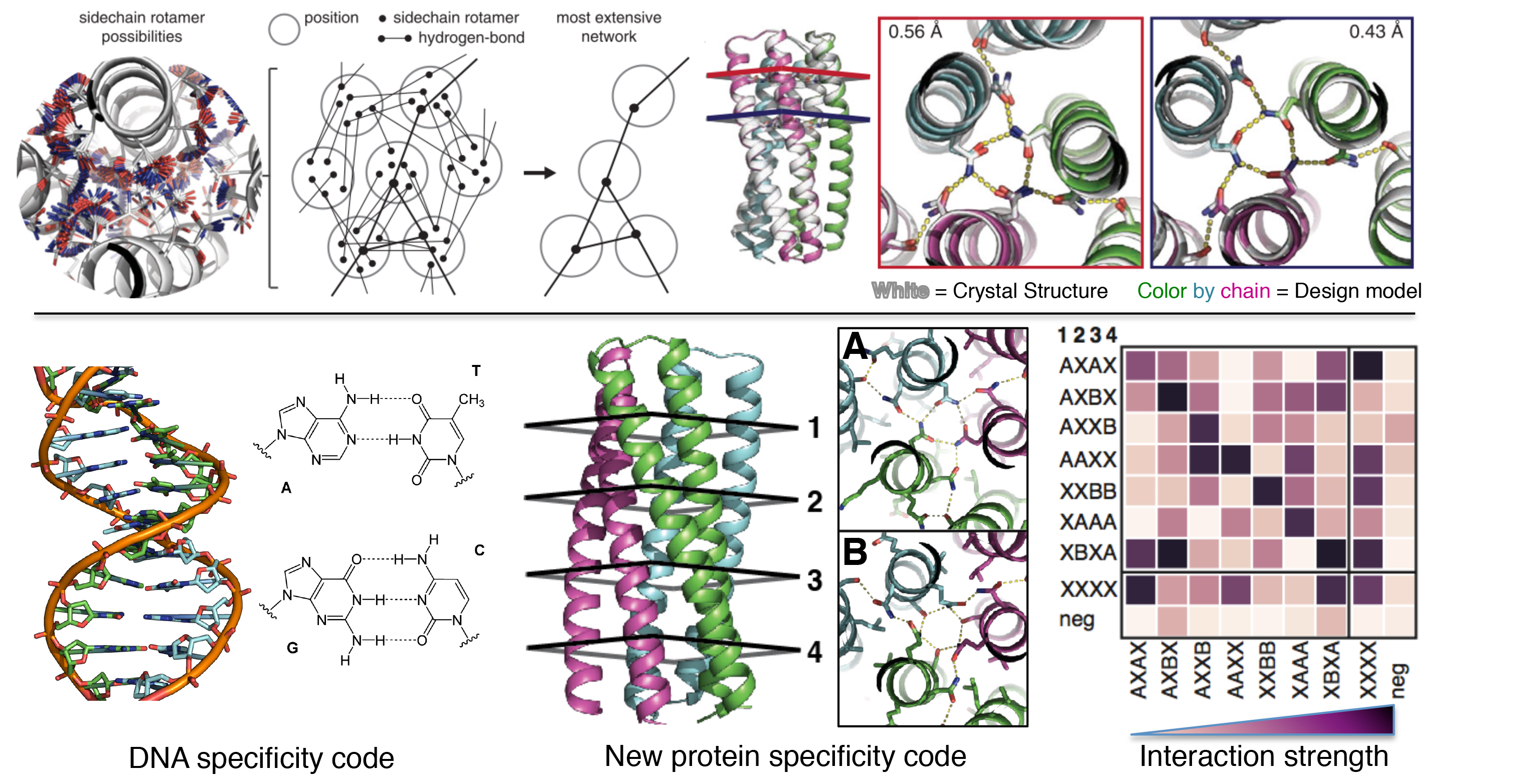
De novo design makes a splash
A paper recently published in Science by several members of the IPD, in collaboration with others, entitled “De novo design of protein homo-oligomers with modular hydrogen-bond network-mediated specificity,” discusses designing proteins in a similar way to DNA so that they may be used to engineer structures. Geekwire has written up a…
-
Foldit Turns 8!
Over the weekend, Foldit had its 8th birthday! In celebration, they will be tweeting (@Foldit) fun facts and infographics on their feed. Haven’t heard of the game or tried playing it yet? What better time than now! Click here to learn more and to join an ever-growing community that spans…