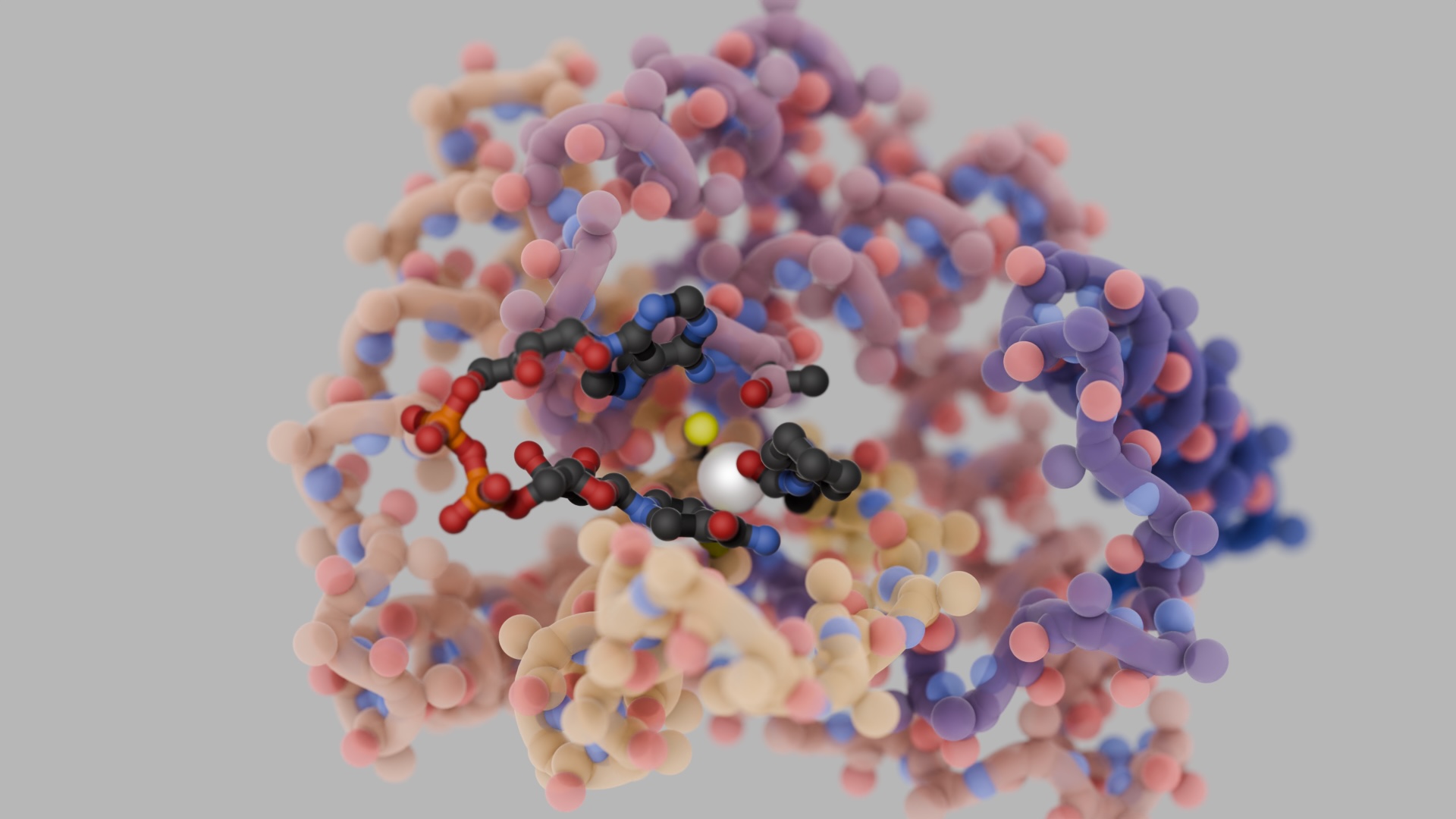
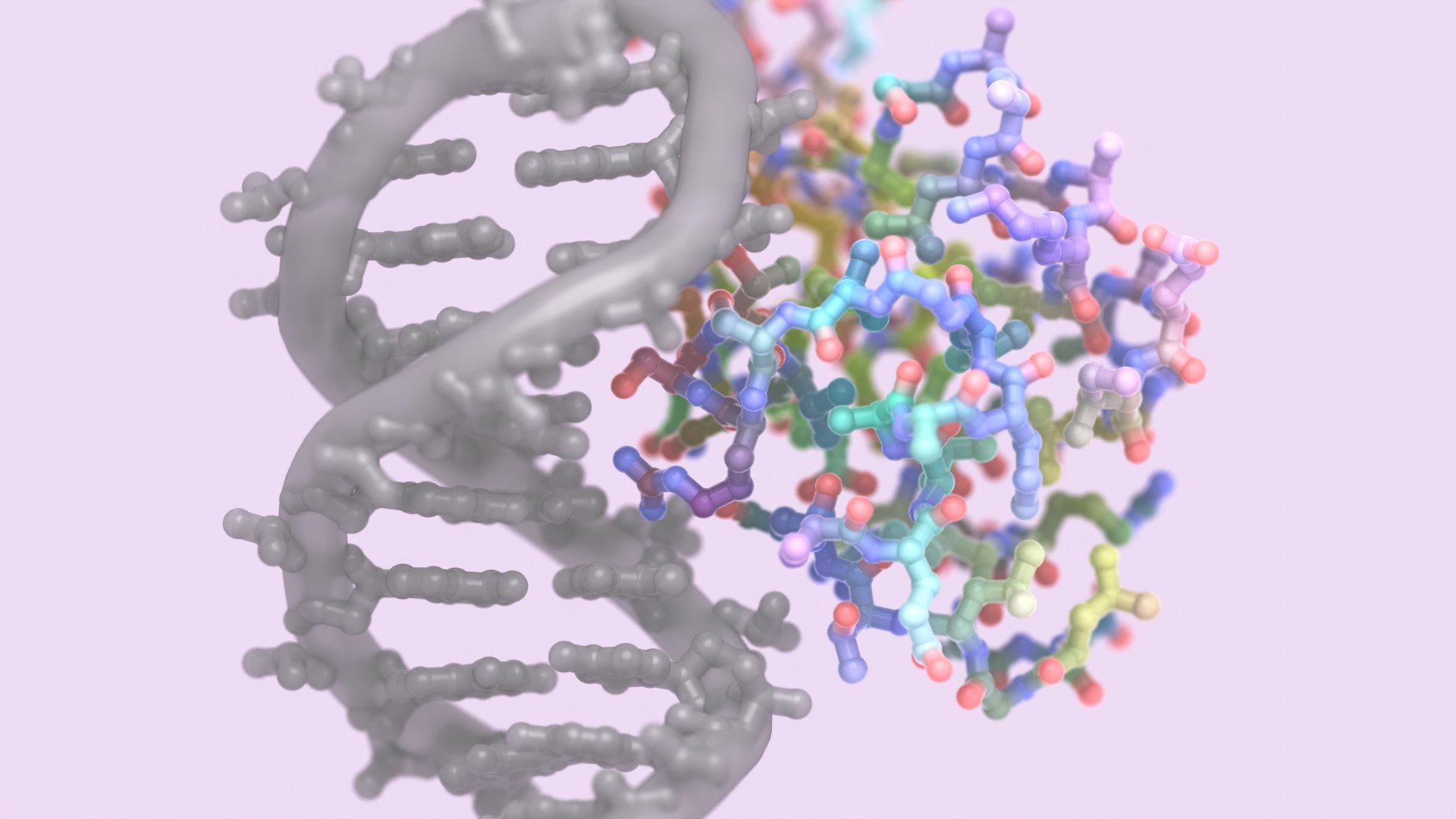
Purification of antibody IgG from crude serum or culture medium is required for virtually all research, diagnostic, and therapeutic antibody applications. Researchers at the Institute for Protein Design (IPD) have used computational methods to design a new protein (called “Fc-Binder”) that is programed to bind to the constant portion of IgG (aka “Fc” region) at basic pH (8.0) but to release the IgG at slightly acidic pH (5.5). Published on-line at PNAS (Dec. 31, 2013), the paper is entitled Computational design of a pH-sensitive IgG binding protein, co-authored by Strauch, E. – M., Fleishman S. J., & Baker D. Learn more at this link.