Latest posts
-
NBC: “Scientists use new A.I. tech to fight diseases”
NBC reports on how our scientists are harnessing artificial intelligence to improve how proteins for medicines and vaccines are developed.
-
Frontiers of Knowledge Award goes to David Baker, Demis Hassabis and John Jumper
The 15th BBVA Foundation Frontiers of Knowledge Award in Biology and Biomedicine has gone to David Baker, Demis Hassabis and John Jumper “for their contributions to the use of artificial intelligence for the accurate prediction of the three-dimensional structure of proteins.” From the BBVA Foundation: Baker – a Professor of…
-
NYT: “A.I. Turns Its Artistry to Creating New Human Proteins”
The New York TImes has reported on how, Inspired by digital image generators like DALL-E, our scientists are building artificial intelligences that can fight cancer, flu and COVID-19.
-
Establishing our first international translational research project
From our partners at the BioInnovation Institute: BioInnovation Institute (BII), an international enterprise foundation with a non-profit objective incubating and accelerating world-class life science research, announces today that it has accepted a new project into its Bio Studio program. Based on recent breakthroughs in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and protein design,…
-
David Baker to present at the NIH Director’s Lecture Series
David Baker presented at the NIH Director’s Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series on December 14, 2022. From the National Institutes of Health: The NIH Director’s Wednesday Afternoon Lecture Series, colloquially known as WALS, is the highest-profile lecture program at the NIH. Traditionally, lectures have occurred on most Wednesdays from September through…
-
A diffusion model for protein design
Update (July 2023): Our manuscript on the development of RFdiffusion has been published in Nature. A team led by scientists from the Baker Lab has created a powerful new way of designing proteins that combines structure prediction networks and generative diffusion models. The team demonstrated extremely high computational success using…
-
ProteinMPNN excels at creating new proteins
Over the past two years, machine learning has revolutionized protein structure prediction. Now, three papers in Science describe a similar revolution in protein design. In the new papers, scientists in the Baker lab show that machine learning can be used to create proteins much more accurately and quickly than previously…
-
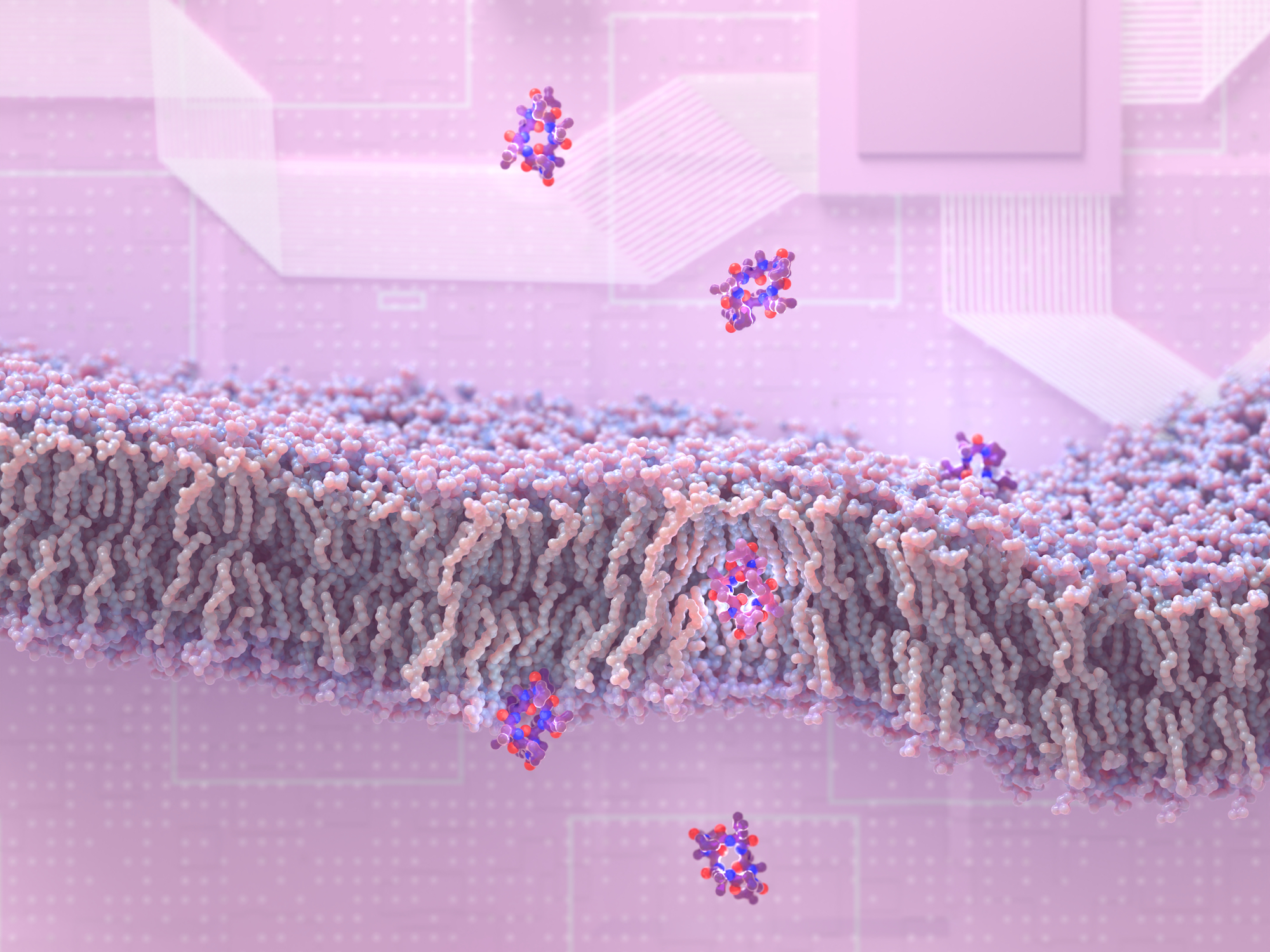
Design of membrane-traversing peptides leads to new spinout
Researchers at the Institute for Protein Design have discovered how to create peptides that slip through membranes and enter cells. This drug design breakthrough may lead to new medications for a wide variety of health disorders, including cancer, infection, and inflammation. This research appears in the journal Cell [PDF]. “This…
-
Annual Report 2022
Protein design reached two major milestones this year: Our Institute succeeded in producing its first fully-approved medicine, and our spinout companies have together raised over one billion dollars in capital. We are pleased to present this overview of the progress made at the Institute for Protein Design during the past…
-
Biosensor startup Monod secures $25M seed financing
Monod Bio, a life sciences company developing custom diagnostic biosensors that emit light to detect specific biomolecules of interest, today announced it has raised a $25M seed financing round. The round was led by Matrix Capital, with participation from the Global Health Investment Corporation, Cercano Management, The Washington Research Foundation,…